Explain Difference Between Independent and Repeated Measures Stats
All three groups are performing a reaction time task before and after the same intervention. From an analysis point of view it doesnt really matter which one you have.
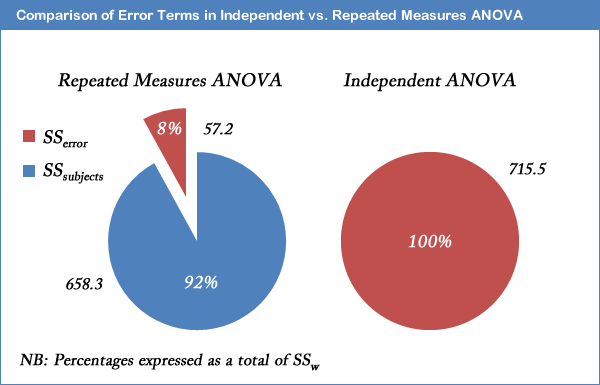
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
1 iv but with 2 levels different in each sample results of test if p-value 005 for 2 tailed h1 we conclude samples come from.
. The distinction is very simple. Replication involves running the same study on. Repeated measures also requires fewer participants as data from all conditions is from the same group of participants.
Each level or related group is a specific time point. An independent samples t-test uses the following test statistic. All three are types of hierarchical nested or multilevel data.
Repeated measures designs can be very powerful because they control for factors that cause variability between subjects. A repeated measures design consists of testing the same individuals on two or more conditions. Repeated-measures design means that the same sample is tested in all of the different treatments.
So if you measured the chips then did something to them then measured them again etc it would be repeated measures. The Benefits of Repeated Measures Designs. For a repeated-measures design the same subjects are used in both treatment conditions.
Again a repeated measures ANOVA has at least 1 dependent variable that has more than one observation. A researcher conducts an experiment comparing two treatment conditions with 20 scores in each condition. Repeated measures involves measuring the same cases multiple times.
However the downfalls of repeated measures are the benefits of independent measures. A repeated-measures a matched-subjects and an independent-measures study all produce a t statistic with df 10. My supervisor insists it is a Split-Plot ANOVA.
This means that each condition of the experiment includes the same group of participants. If a repeated-measures design is used how many participants are needed for the study. Thanks to the greater statistical power a repeated measures design can use fewer subjects to detect a desired effect size.
In a repeated measures case the same subjects are being tested under different conditions. Repeated Measures design is also known as within groups or within-subjects. 1 The difference between repeated measures and independent measures designs Experimental designs with ---------------are called independent measures designs Experimental designs with ---------------are called repeated measures Expert Answer 100 42 ratings In independent measures design different participants are used in each conditio.
The data are the same for both analyses and the differences between samples are the same -1162. Why should you use ANOVA instead of several t tests to evaluate mean differences when an experiment consists of three or more treatment conditions. Psy201 Stats Ch 10 - Independent measures test.
Independent-measures design or between-subjects design means that there is a separate sample for each of the treatments being compared. It can be hard to distinguish between repeated measures and longitudinal data if the repeated measures occur over time. In an independent groups test the subjects in the 2 groups or conditions t test or 3 groups 4 groups 5 groups.
Step-by-step solution 100 9 ratings for this solution Chapter 11 Problem 3P is solved. Explain the difference between a matched-subjects design and a repeated-measures design. Independent sample t-tests summary used to compare data from two samples with different participants in each sample samples can contain different numbers of participants.
Repeated Measures design is an experimental design where the same participants take part in each condition of the independent variable. Explain the difference between a matched-subjects design and a repeated-measures design. Click to see full answer Regarding this what is an independent measures design.
The advantage of this is that individual differences between participants are removed as a potential confounding variable. Test statistic t x1 x2 d s21 n1 s22 n2. They are the same people.
A prepostfollowup design is a classic example. Or 3 conditions 4 conditions are different people. A repeated measures ANOVA model can also include zero or more independent variables.
The 2-sample t-test uses a sample size of 30 two groups with 15 per group while the paired t-test has only 15 subjects but the researchers test them twice. The repeated measures ANOVA compares means across one or more variables that are based on repeated observations. View this answer View a sample solution Step 1 of 2 Step 2 of 2 Back to top Corresponding textbook Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences 7th Edition.
If an independent-measures design is used how many participants are needed for the study. A repeated measures design consists of testing the same individuals on two or more conditions. PSY 201 Ch 11 - Repeated Measures.
It does not interrogate. In repeated measures ANOVA the independent variable has categories called levels or related groups. 1 dv measured in both samples.
Where measurements are repeated over time such as when measuring changes in blood pressure due to an exercise-training programme the independent variable is time. This is advantageous because fewer participants are needed to run an experiment. I thought this analysis was simply a 3 group by 2 pre- post Repeated Measures ANOVA.
Order effects are more likely to occur because participants will have had the opportunity to learn the tests that may be used. In contrast to an independent measures design a repeated measures design has only one group of participants who complete every research condition. An independent measures design consists of using different participants for each condition of the experiment.
This makes a repeated measures design seem far superior to an independent measures design. The independent ANOVA or simple ANOVA is not appropriate for repeated measurements on the same subjects as the data violates the assumption of independence ie. Also repeated measures is more time and cost effective because participants are used in more than one condition.
How does a Split-Plot ANOVA differ from a RM ANOVA particularly in this context. I have three independent groups. How many participants were used in each study.
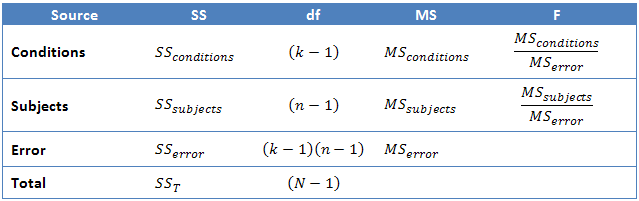
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics

One Way Anova Vs Repeated Measures Anova The Difference
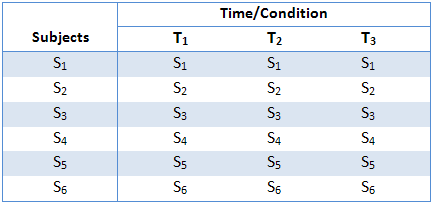
Repeated Measures Anova Simple Introduction

Repeated Measures Anova Spss Statistics Anova Statistical Data
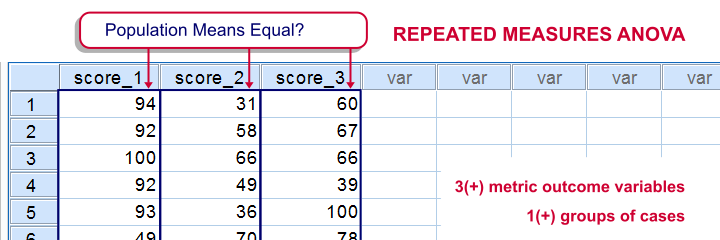
Repeated Measures Anova Simple Introduction
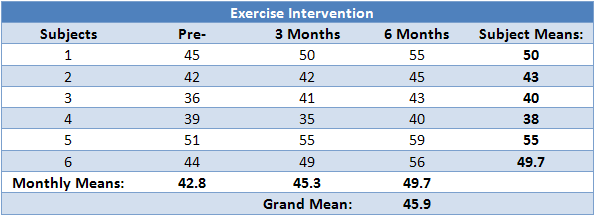
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
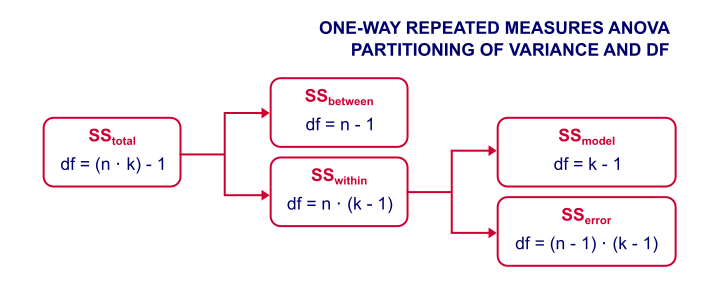
Repeated Measures Anova Simple Introduction

Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
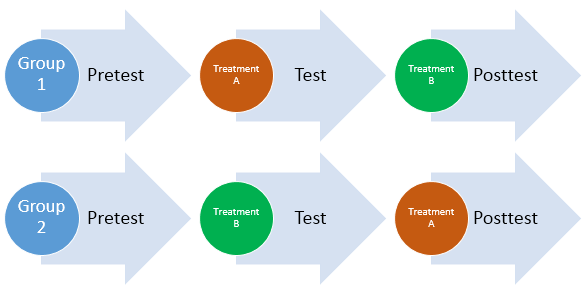
Repeated Measures Designs Benefits Challenges And An Anova Example
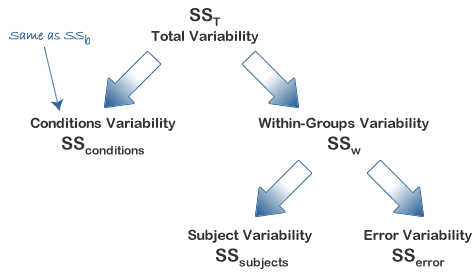
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics

Experimental Design Simply Psychology
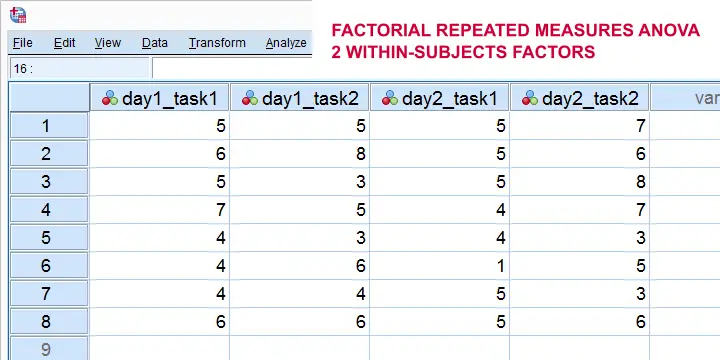
Spss Repeated Measures Anova 2 Within Subjects Factors
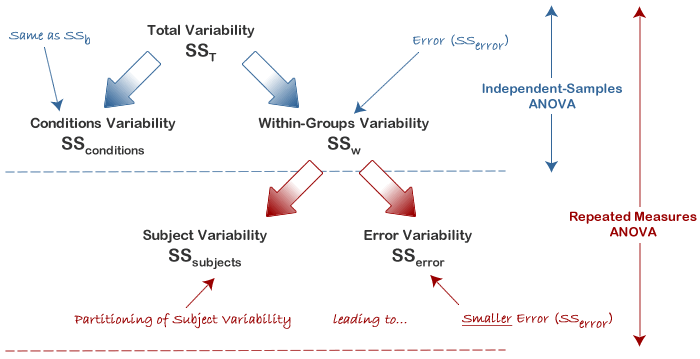
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
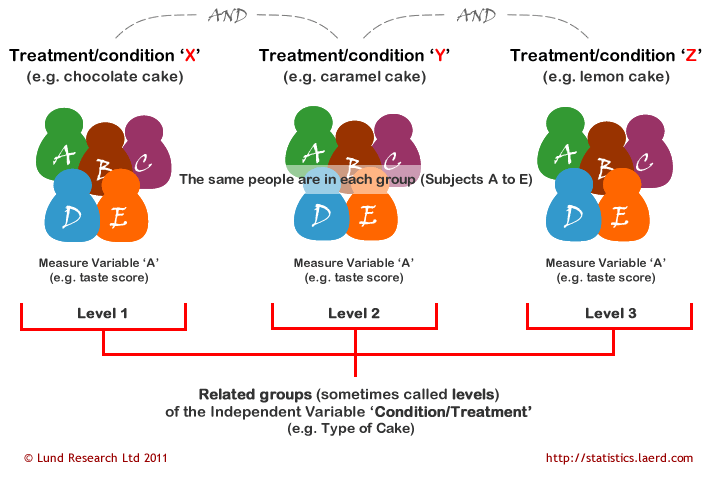
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
Repeated Measures Anova In Spss Including Interpretation Easy Spss Tutorial
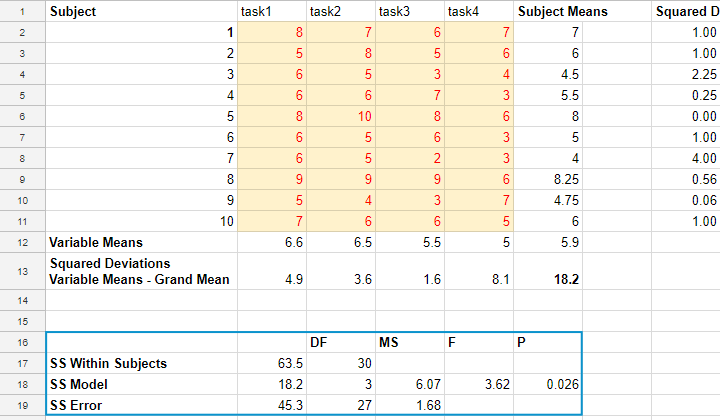
Repeated Measures Anova Simple Introduction
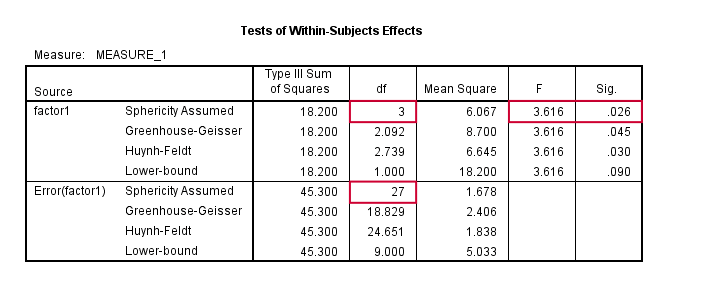
Repeated Measures Anova Simple Introduction
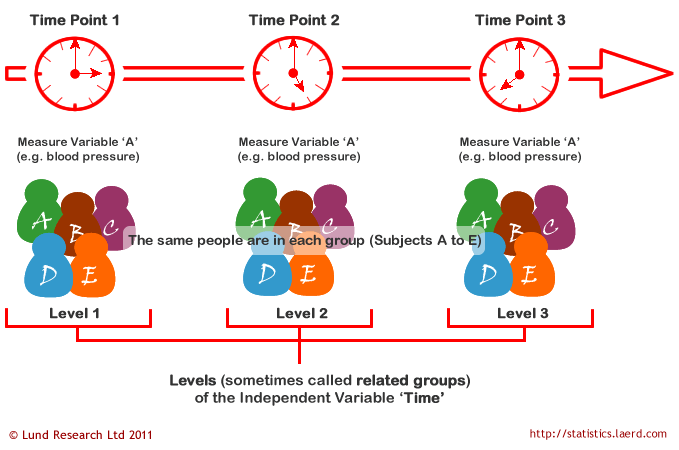
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
Conduct And Interpret A Repeated Measures Ancova Statistics Solutions
Comments
Post a Comment