Ionization Energy Is Best Described as
Ionization energy or ionisation energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. The strength of the electric field surrounding an ion 25.

Periodic Trends Ionization Energy Explained With Exceptions Study Chemistry With Us Youtube
The ionization energy IE of an atom is the energy required to strip it of an electron.
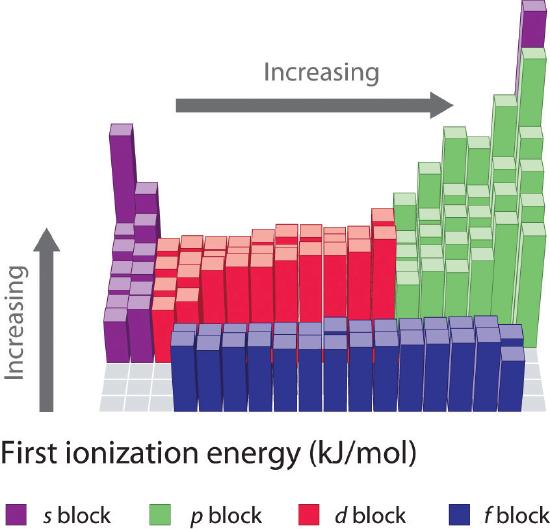
. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom d. Which ion was formed by providing the second ionization energy to remove an electron. The ionization energy of an element increases as one moves across a period in the periodic table because the electrons are held tighter by the higher effective nuclear charge.
The process by which the first ionization energy of hydrogen is measured would be represented by the following equation. Create a table with. In physics and chemistry ionization energy IE American English spelling ionisation energy British English spelling is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated neutral gaseous atom or molecule.
Atomic radius is the measure of the size of an atom. Which element has the smallest atomic radius. The second ionization energy of an element will be higher than the first ionization energy.
H g H g e -. An estimate of the radius or distance between the nucleus and the electron on the furthest occupied shell. Because oxygen is the highest and rightmost element of those listed it will have the highest first ionization energy.
The closer and more tightly bound an electron is to the nucleus the more difficult it will be to remove and the higher its ionization energy will be. The atom will become a cation and has an excess of proton thus it will be positively charged. Ionization energy usually removes the most loosely bound valence electron.
The electronegativity difference between two elements c. Since one two or more electrons can be removed from an atom many ionization energy is possible of that atom. Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in a gas phase.
Energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gas phase. The ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from its orbital around an atom to a point where it is no longer associated with that atom. The electrical voltage produced when an atom is converted into an ion b.
Determination of ionization energies. It is quantitatively expressed as Xg energy X g e. There you can find the metals semi-conductors non-metals inert noble gasses Halogens Lanthanoides Actinoids rare earth elements and transition metals.
The atom will become a cation and has an excess of proton thus it will be positively charged. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a specific atom. The ionization energies associated with some elements are described in the Table 1.
1 It is quantitatively expressed as. 119 rows The unity for ionization energy is eV. Ionization energy is the energy kJ required for the complete removal of 1 mol of valence electrons from 1 mol of gaseous atoms or ions.
An atoms ionization energy may be best described as which one of the following. Ionization energy usually removes the most loosely bound valence electron. M g M g e IE.
Ionization energy usually removes the most loosely bound valence electron. More generally the nth ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to strip it of an nth electron after the first n-1 have already been removed. The ionization energy or ionization potential is the energy required to completely remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion.
The ionization energy IE or ionization potential is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state. Which element would most likely have a positive electron affinity. In physics and chemistry ionization energy IE American English spelling ionisation energy British English spelling is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated neutral gaseous atom or molecule.
Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in a gas phase. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system. The ionization energy of an element is a measure of how easily it forms a cation.
Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in a gas phase. Which best describes ionization energy. Up to 10 cash back Ionization energy is a property of an atom or ion that describes the lowest energy needed to remove a electron from it in the ground state.
The atom will become a cation and has an excess of proton thus it will be positively charged. 2 Use a valid data source to find a list of the first ionization energy for each of the elements in the third period. It is measured in kJmol which is an energy unit much like calories.
For any given atom the outermost valence electrons will have lower ionization energies than the inner-shell kernel electrons. By definition the first ionization energy of an element is the energy needed to remove the outermost or highest energy electron from a neutral atom in the gas phase. Ionization energy increases up and to the right on the periodic table.
Ionization energy by definition is the energy required to move an electron from a gaseous atom or ion.

Ionization Energy Electrical4u

Periodic Trends Made Easy Chemtalk

What Is Oxygen Ionization Energy

Periodic Trends Ionization Energy Chemistry For Non Majors
Answer In General Chemistry For John 160884
Lab On Graphing And Analyzing Ionisation Energies By Jason Liu The Shadow Medium

Ionization Energy Introduction To Chemistry
Lab On Graphing And Analyzing Ionisation Energies By Jason Liu The Shadow Medium

Lesson Explainer Ionization Energy Nagwa

Ionization Energy Formula Definition Concepts And Examples
How To Describe The Trends In The First Ionization Energy Within Groups And Across Periods In The Periodic Table Can You Provide An Example Quora

How To Describe The Trends In The First Ionization Energy Within Groups And Across Periods In The Periodic Table Can You Provide An Example Quora
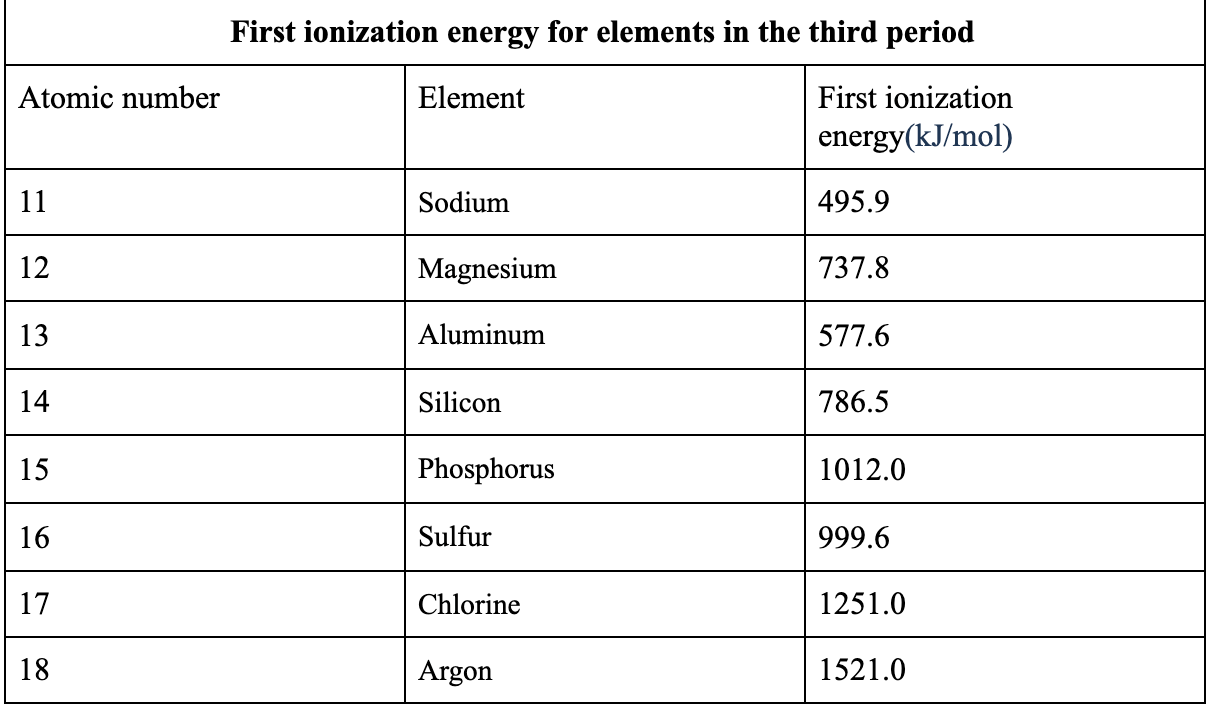
Lab On Graphing And Analyzing Ionisation Energies By Jason Liu The Shadow Medium
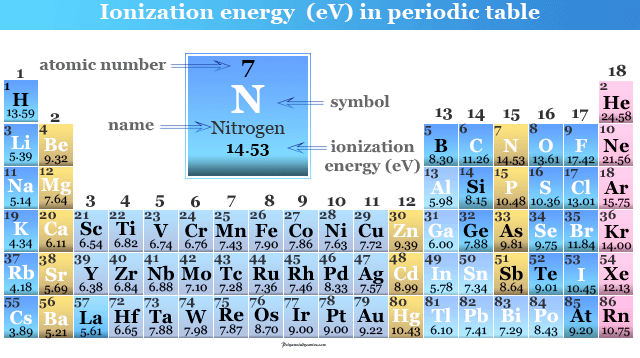
Ionization Energy Definition Equation Periodic Table Trends

7 4 Ionization Energy Chemistry Libretexts

Ionization Energy Periodic Table Trends Chemtalk

Ionization Potential Definition Periodic Variation Questions Answers
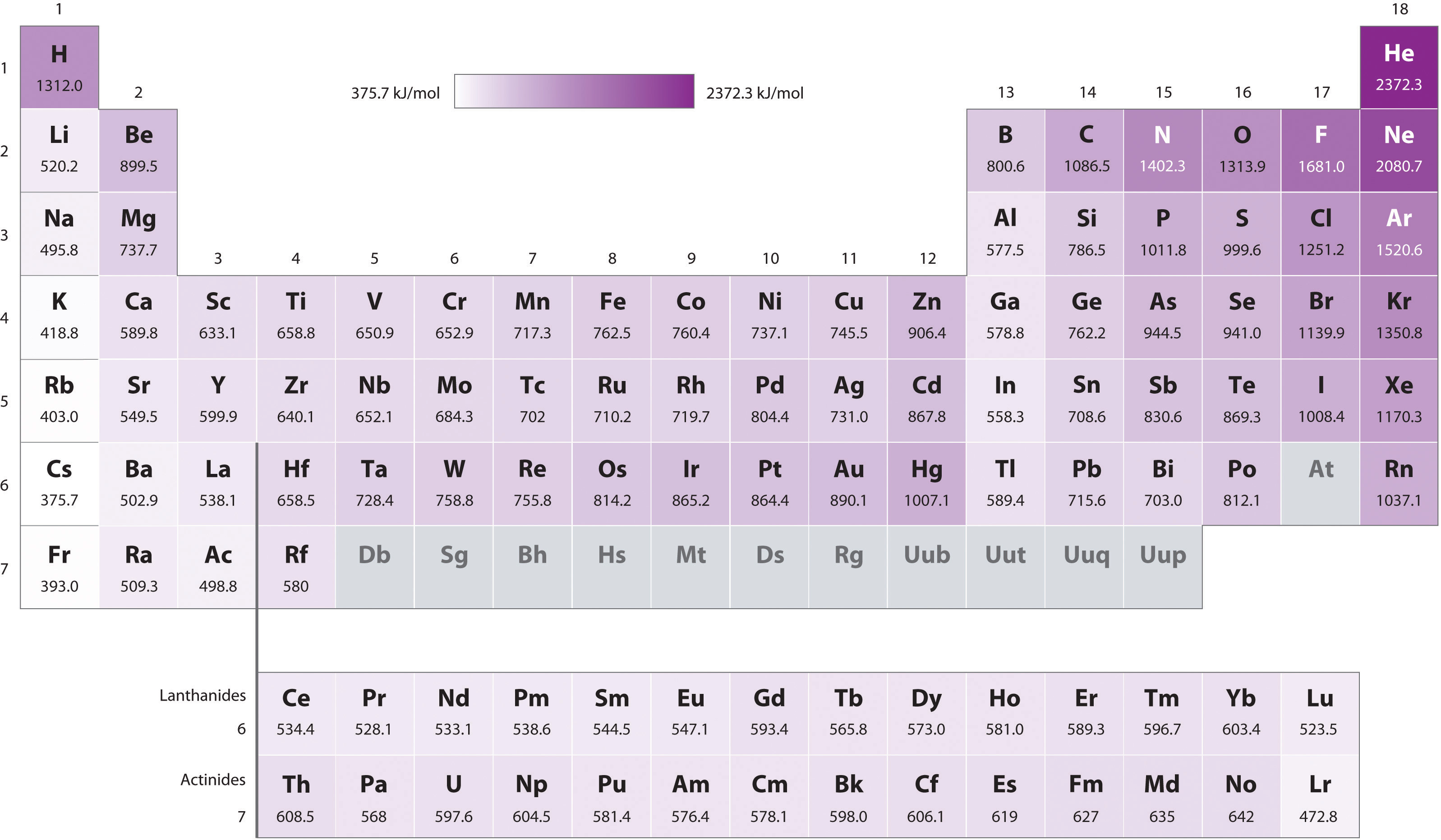
7 4 Ionization Energy Chemistry Libretexts
What Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic Radii Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity Socratic
Comments
Post a Comment